Windows Hello for Business (WHfB) is a cornerstone of Microsoft’s modern security approach, eliminating traditional passwords in favor of biometric and PIN-based authentication. For enterprises using a hybrid environment—with both on-prem Active Directory and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)—implementing WHfB ensures strong authentication, seamless access, and Zero Trust compliance.
This comprehensive guide walks you through everything you need to deploy Windows Hello for Business in a hybrid setup—covering architecture, configuration, screenshots, and best practices for IT administrators.
Why Set Up Windows Hello for Business?
Traditional passwords are a weak link in modern security. According to Microsoft, over 80% of data breaches are caused by stolen or compromised credentials. WHfB replaces them with two-factor authentication backed by hardware-level protection like TPM chips. This not only enhances security but improves login speed and user satisfaction.
- Eliminates phishing and credential theft risks
- Integrates with Azure AD, Intune, and Group Policy
- Supports Zero Trust architecture
- Complies with security frameworks like NIST and ISO 27001
Understanding the Windows Hello for Business Architecture
In a hybrid model, WHfB bridges on-premises Active Directory and Azure AD to provide secure, passwordless authentication. The system issues cryptographic keys to each device and user, which are validated during sign-in.
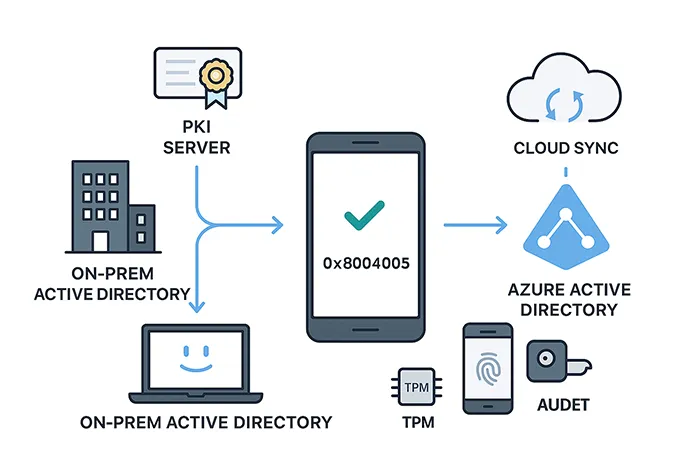
Key Components
- Azure Active Directory: Cloud identity provider for modern authentication.
- On-Premises AD: Legacy domain management and GPO control.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): For certificate trust deployments.
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM): Hardware-based key storage.
Prerequisites for Hybrid WHfB Deployment
- Windows 10 version 1709 or later (Windows 11 recommended)
- Azure AD Connect configured with device writeback
- Enterprise CA (for certificate trust)
- GPO or Intune readiness
- Hybrid Azure AD Join enabled
Step-by-Step Setup: Windows Hello for Business in a Hybrid Environment
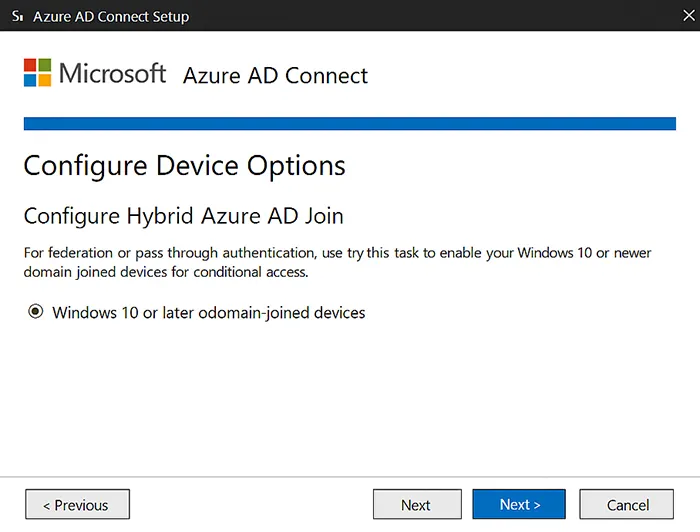
Step 1: Enable Device Registration with Azure AD Connect
Ensure that Azure AD Connect is configured correctly.
- Launch Azure AD Connect on your server.
- Select Configure Device Options.
- Choose Configure Hybrid Azure AD Join.
- Follow the prompts and complete setup.
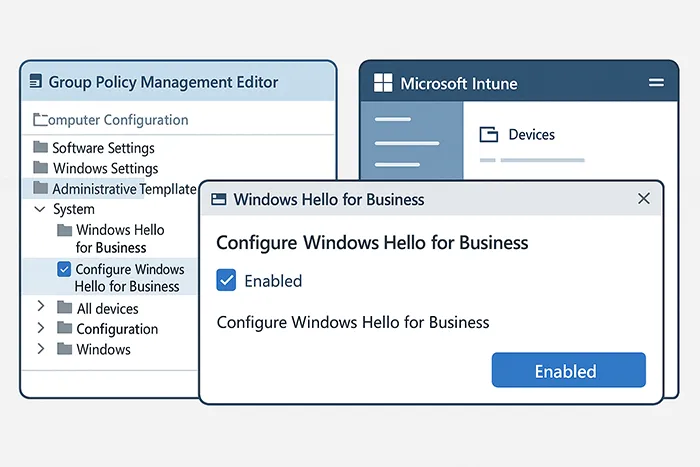
Step 2: Configure Policies Using Group Policy or Intune
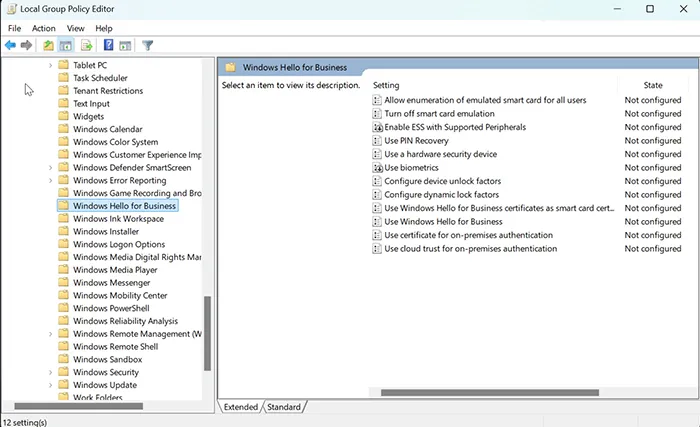
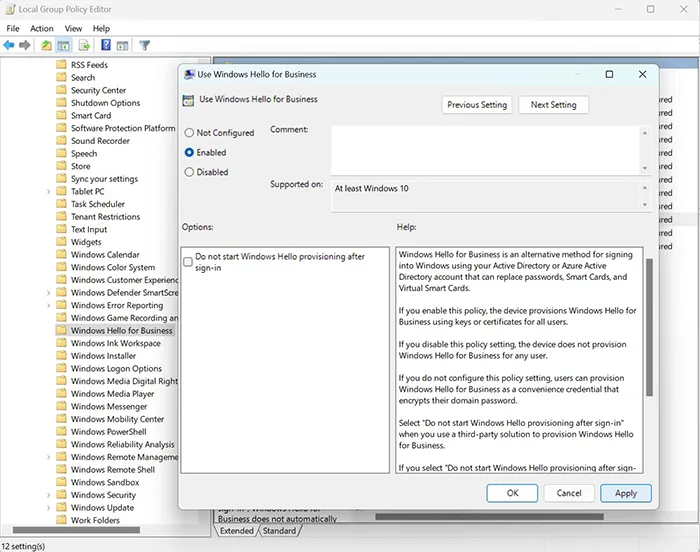
Option A: Using Group Policy
- Open Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).
- Navigate to:
Computer Configuration → Administrative Templates → Windows Components → Windows Hello for Business. - Enable the policy: Use Windows Hello for Business.
Option B: Using Intune
- Sign in to Intune Admin Center.
- Go to Devices → Configuration Profiles → + Create Profile.
- Set Platform: Windows 10 and later.
- Profile Type: Identity Protection.
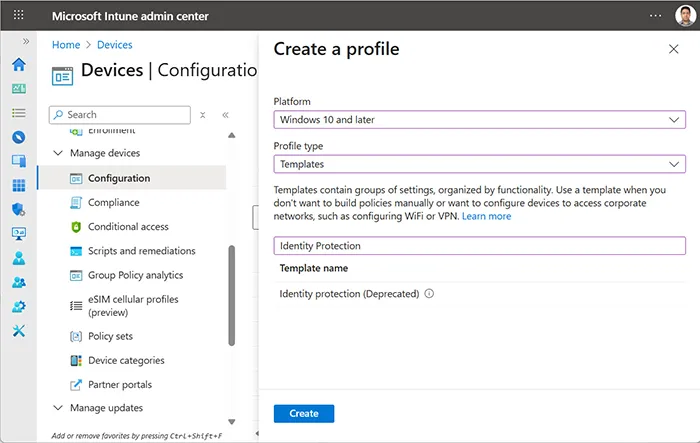
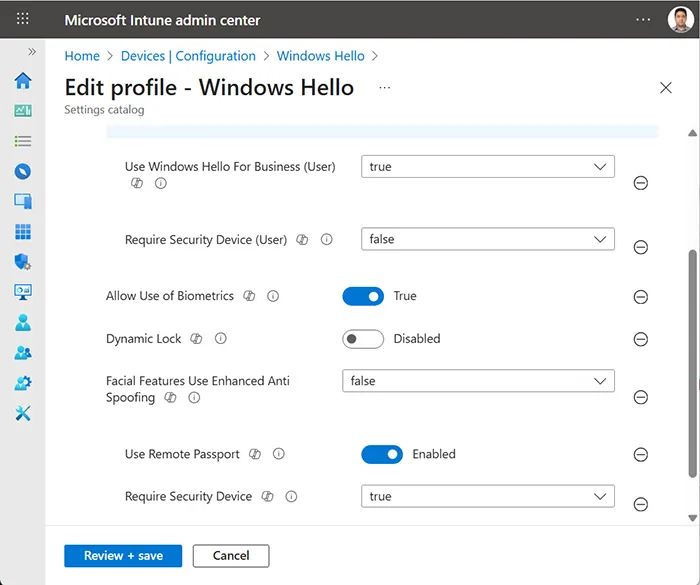
Inside the profile, under Configure Windows Hello for Business, select “Enable” and save.
Step 3: Choose Between Key Trust and Certificate Trust
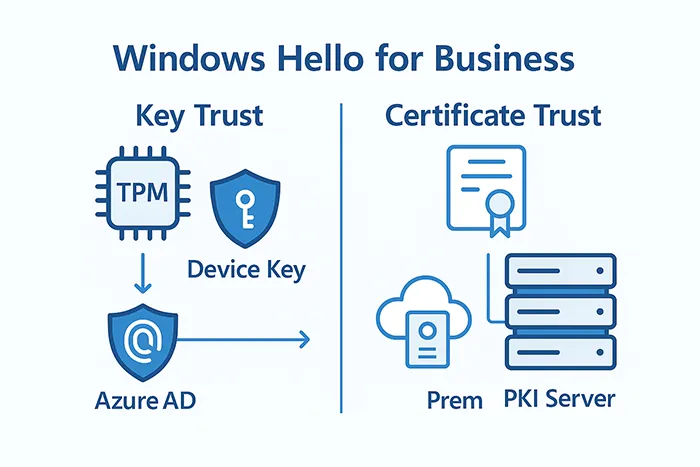
- Key Trust: Simplified setup, no PKI requirement, recommended for cloud-first organizations.
- Certificate Trust: Requires enterprise PKI, preferred for regulated industries needing smartcard equivalence.
Step 4: Verify Setup and Monitor Performance
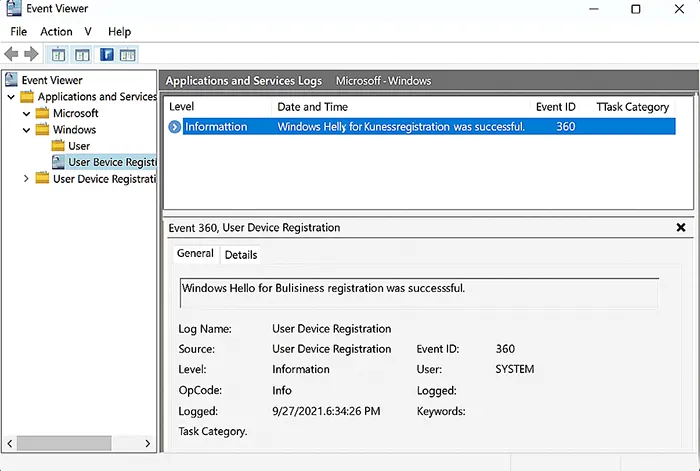
- Open Event Viewer →
Applications and Services Logs → Microsoft → Windows → User Device Registration. - Look for Event ID 360 (successful registration).
- Check Azure AD Sign-in Logs for device registration success.
Step 5: Monitor, Troubleshoot, and Audit

- Use Azure AD audit logs to detect registration failures.
- Verify TPM chip health and device attestation.
- Test fallback methods like PIN sign-in.
Best Practices for a Successful Rollout
- Start with a pilot group before enterprise-wide deployment.
- Educate users on passwordless sign-in and backup options.
- Regularly review compliance with your Zero Trust framework.
- Use Intune reports to identify devices missing WHfB registration.
Final Thoughts
Deploying Windows Hello for Business in a hybrid environment bridges modern cloud identity with on-prem legacy systems, improving both security and user experience. Whether you’re managing Intune devices or GPO-managed workstations, WHfB provides a strong foundation for a passwordless, Zero Trust future.
For more enterprise IT automation insights, check out The Future of Network Automation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between key trust and certificate trust?
Key trust uses TPM-stored keys and doesn’t require PKI, while certificate trust uses user certificates issued from a CA—ideal for smartcard-equivalent scenarios.
Can I deploy WHfB without Azure AD?
Yes, but it’s less common. Fully on-prem setups using certificate trust are supported but lack modern Azure-based policy control.
Is TPM required for Windows Hello for Business?
TPM is recommended for hardware-level security. Without TPM, credentials are stored in software, slightly reducing security strength.
How can I monitor WHfB deployment success?
Use Event Viewer (Event ID 360) and Azure AD Sign-in logs to confirm device registration and authentication events.
Can I manage WHfB policies via both Intune and GPO?
To avoid conflicts, use one management method—Intune for cloud-first devices, GPO for on-prem domain-joined systems.