A Look Back: The Journey of Cloud Computing
From Shared Resources to SaaS
In the early days of computing during the 1960s, John McCarthy coined the idea of “computing as a utility.” This laid the foundation for shared computing resources. By the 1990s, the rise of the internet provided the infrastructure for modern cloud services.
The 2000s marked a turning point. Salesforce pioneered the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model, while Amazon Web Services (AWS) introduced Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), enabling businesses to scale on demand and pay only for what they used.
The Hybrid Era
By the 2010s, businesses began combining on-premises data centers with public cloud platforms, creating hybrid environments. This was made possible through innovations like Docker and Kubernetes, which simplified containerized applications and improved scalability.
Today, organizations live in a multi-cloud world, using services from AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud simultaneously while integrating AI and machine learning into everyday workflows.
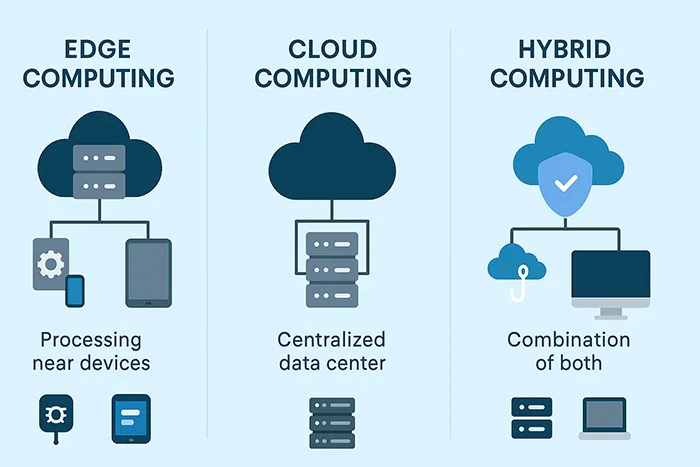
Trends Shaping Cloud Computing Today
⭐ Edge Computing
In scenarios like self-driving cars, waiting for cloud data can introduce dangerous delays. Edge computing solves this by processing data closer to the source, enabling real-time decisions.
⚡ Serverless Architectures
Technologies like AWS Lambda allow developers to focus on code while the cloud provider handles server management. This pay-per-execution model boosts agility, scalability, and cost efficiency.
🌱 Green Cloud Initiatives
Cloud providers are under pressure to reduce carbon footprints. Google Cloud is pushing toward running its data centers on 24/7 carbon-free energy. Similarly, Microsoft’s Azure sustainability commitments aim for carbon-negative operations by 2030.

🔒 Enhanced Security
With cyber threats increasing, Zero Trust security and AI-powered monitoring are becoming the standard. For enterprises, Zero Trust ensures no access is granted without verification, even inside corporate networks.
The Road Ahead: What to Expect
🔬 Quantum Cloud Computing
Quantum cloud services are being explored by IBM, Google, and Microsoft. This technology promises exponential processing power, revolutionizing industries like drug discovery, cryptography, and logistics optimization.

🔧 Cloud-Native Applications
New apps are being developed as cloud-native, designed for scalability, speed, and resilience from the ground up, leveraging containers and DevOps pipelines.
🤖 AI-Driven Cloud Services
Expect predictive analytics, smart automation, and real-time decision-making to be embedded directly into cloud services. This will redefine how businesses operate.
🌍 Expanding into Developing Markets
Cloud expansion into underserved regions ensures innovation and opportunities for startups, enabling global digital equity.
🎮 Immersive Technologies
Future AR and VR applications will rely heavily on cloud scalability for gaming, education, and enterprise collaboration.

🏛️ Sovereign Cloud & Compliance
As regulations tighten, enterprises face pressure to ensure compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. Sovereign clouds are emerging to meet these regional and industry-specific compliance requirements.

Challenges in Cloud Adoption
- Data Privacy: Compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA remains a top challenge.
- Vendor Lock-in: Migrating between providers can be costly and complex.
- Skill Gaps: The demand for cloud architects and engineers continues to exceed supply.
Why It Matters
For enterprises, cloud adoption isn’t just about saving costs—it’s about gaining a competitive edge. Startups leverage the cloud to scale rapidly, while enterprises use AI-powered analytics to drive innovation across finance, healthcare, and education.
Imagine healthcare without cloud-based diagnostics or eCommerce without scalable infrastructure—it would cripple entire industries.
So, Where Does This Leave Us?
The cloud has moved beyond simple storage. Today, it’s about creating opportunities, solving global challenges, and innovating at scale. The next time you stream a movie or use Windows Hello for Business, remember: you’re experiencing the invisible power of the cloud.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the cloud?
The cloud refers to servers accessed over the internet to store, process, and manage data instead of relying solely on local devices.
Is cloud computing secure?
Yes, when platforms implement industry standards such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and Zero Trust frameworks.
Can I lose data stored in the cloud?
While rare, data loss is possible. However, top providers like Microsoft and Google offer redundancy, failover systems, and backup solutions.
What is multi-cloud?
Multi-cloud refers to using services from more than one provider to balance flexibility, performance, and cost.
How do I get started with cloud computing?
Explore services like Azure Active Directory, AWS, or Google Cloud. Many offer free tiers and certifications for beginners.