Cybersecurity threats are growing more sophisticated every day, from Remote Access Trojans to large-scale ransomware attacks. Traditional security measures alone are no longer enough. That’s where Artificial Intelligence (AI) is stepping in. By leveraging machine learning, automation, and behavioral analytics, AI is transforming how organizations detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats.

Why AI Matters in Cybersecurity
Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their methods. Phishing emails, advanced malware, and zero-day vulnerabilities can bypass traditional defenses. AI-powered tools can:
- Analyze vast amounts of network traffic in real time
- Identify anomalies that may indicate attacks
- Predict potential threats before they cause damage
- Automate responses to reduce human workload
AI-Powered Threat Detection
Unlike signature-based detection methods that rely on known patterns, AI systems use behavioral analysis and machine learning to detect suspicious activities. For example, if an employee’s account suddenly attempts thousands of logins, AI can flag and block the activity instantly.

AI in Security Operations Centers (SOCs)
Security Operations Centers (SOCs) are overwhelmed with alerts. AI reduces noise by filtering false positives and prioritizing genuine threats. This helps analysts focus on real issues and respond faster, lowering the mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to respond (MTTR).

Automated Cyber Defense
AI is not just about detection—it’s also about action. With automated defense, AI can:
- Quarantine infected devices before malware spreads
- Block suspicious IPs and domains automatically
- Update firewall and endpoint rules in real time
- Generate forensic reports for compliance
This aligns with Zero Trust Security principles, ensuring no user or device is inherently trusted.
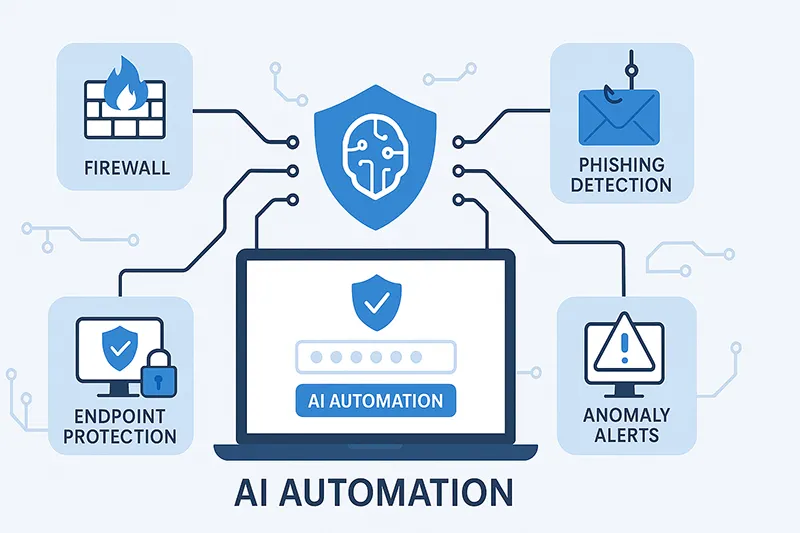
Use Cases of AI in Cybersecurity
- Phishing Detection: AI scans emails for malicious intent, catching sophisticated scams.
- Fraud Prevention: Banks use AI to analyze unusual spending patterns.
- Endpoint Security: AI enhances antivirus and anti-malware tools with predictive capabilities.
- Cloud Security: AI protects workloads across multi-cloud environments.
Challenges of Using AI in Cybersecurity
While powerful, AI also has challenges:
- Adversarial Attacks: Hackers may try to manipulate AI models.
- Bias & Errors: Poor training data can lead to false positives or missed threats.
- High Costs: Advanced AI security solutions may be expensive for smaller businesses.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
Looking ahead, AI will play an even bigger role in cybersecurity by integrating with:
- Biometric authentication for identity verification
- AI-driven compliance monitoring for GDPR and upcoming AI Act regulations
- Autonomous SOCs where AI handles most alerts without human intervention

Related Articles
- AI in IT Operations: Use Cases and Benefits
- Protecting Your Personal Computer from Remote Access Trojans
- What is Zero Trust Security?
- Comprehensive Guide to Removing Malware and Viruses
Frequently Asked Questions
Can AI completely replace human cybersecurity experts?
No. AI enhances security but humans are still needed for decision-making and oversight.
Is AI in cybersecurity affordable for small businesses?
Yes. Many vendors now offer affordable, cloud-based AI security tools suitable for SMEs.
Can hackers use AI for cyberattacks?
Yes. Cybercriminals are also using AI for phishing, deepfakes, and evasion tactics.
What is the biggest benefit of AI in cybersecurity?
The ability to detect and respond to threats in real time with minimal human delay.
How does AI support Zero Trust Security?
AI helps enforce Zero Trust by continuously validating user and device behavior before granting access.