Network automation is reshaping how IT professionals manage infrastructure—replacing repetitive manual tasks with intelligent, efficient processes. With the rise of AI, cloud, and hybrid environments, businesses are turning to automation not just for convenience but for survival in an increasingly complex digital world.
What is Network Automation?
Network automation refers to using software to configure, manage, test, and operate network devices and services with minimal human intervention. Instead of relying on manual scripts or repetitive command-line inputs, automation enables centralized, policy-based orchestration across complex infrastructures. According to Gartner, by 2025, more than 60% of enterprises will adopt automation to boost efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance security.
Why Network Automation Is the Future
Organizations are embracing automation for several mission-critical reasons:
- Complex Environments: Multi-cloud and hybrid infrastructures require dynamic, scalable configurations.
- Cybersecurity: Automation enables real-time threat detection and response. Learn more about cybersecurity tools every business needs.
- Bandwidth Demands: AI-driven load balancing optimizes traffic across devices and geographies. See our guide on AI in IT operations.
- Cost Reduction: Fewer human errors and automated provisioning cut operational expenses significantly.
Key Technologies Powering Network Automation
1. Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
AI and ML are at the heart of next-generation automation. From anomaly detection to predictive maintenance, AI enables networks to self-heal and adapt. Cisco reports that AI-driven troubleshooting can reduce issue resolution time by up to 80%.
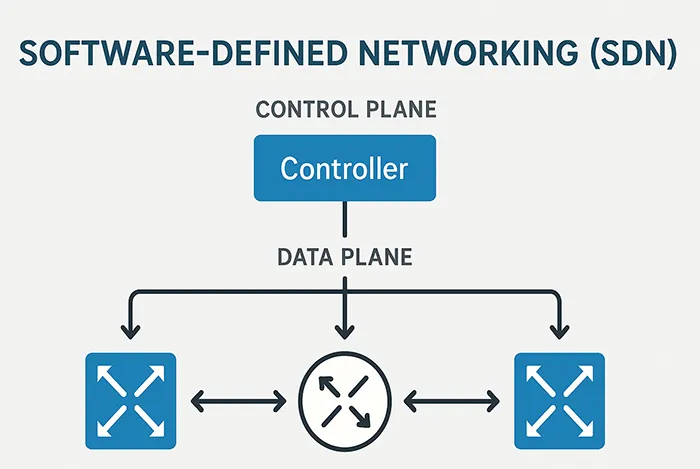
2. Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
SDN decouples the control plane from the hardware, allowing admins to centrally manage traffic and policies. This separation increases agility and simplifies complex enterprise networking.
3. Intent-Based Networking (IBN)
IBN applies high-level business policies and translates them into automated network configurations, ensuring compliance in real-time across enterprise systems.
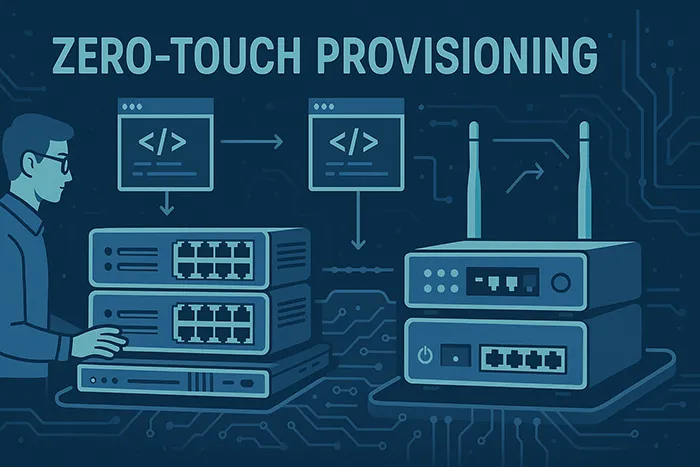
4. Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP)
ZTP allows devices to configure themselves automatically as soon as they connect to the network, eliminating hours of manual setup. This accelerates deployments for data centers, enterprises, and service providers.
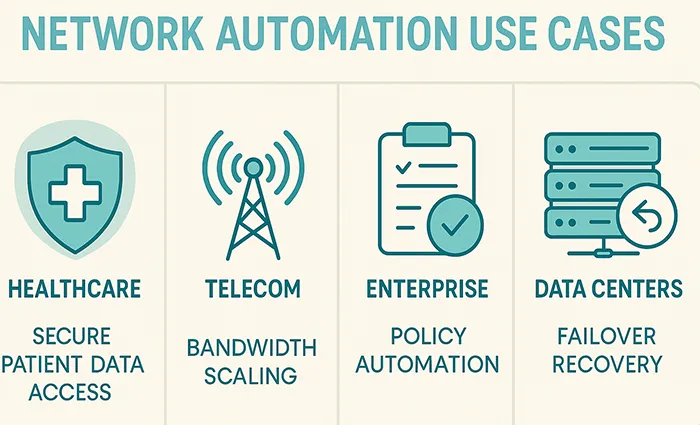
Use Cases of Network Automation
Automation is not just a theoretical upgrade. It’s already delivering tangible value across industries:
- Telecom: Scale bandwidth automatically during peak usage hours.
- Enterprises: Enforce compliance policies and reduce costly misconfigurations.
- Healthcare: Guarantee secure, real-time access to patient data over isolated VLANs. See our related guide on protecting against RAT threats.
- Data Centers: Automate workload balancing, failure recovery, and multi-cloud traffic routing.
Challenges in Implementing Network Automation
While the advantages are clear, enterprises often encounter challenges:
- Legacy Systems: Older infrastructure may not support modern automation APIs or orchestration tools.
- Skill Shortages: IT teams must acquire new scripting, DevNet, and AI monitoring skills.
- Security Risks: Poorly written scripts can introduce vulnerabilities or outages. Learn how to protect networks from RAT-based attacks.
What’s Next: The Future of Network Automation
By 2030, experts predict networks will become fully autonomous. AI and blockchain will merge to create self-verifying, self-configuring, and fully transparent infrastructures. Businesses will gain unprecedented agility and resilience.
Already, companies like Juniper Networks, Google Cloud, and Nokia are rolling out autonomous solutions powered by machine learning and telemetry.
Industry Momentum: Who’s Leading the Charge?
In 2023–2024, enterprises that deployed network automation reported significant gains:
- 40% reduction in downtime
- 30% boost in IT staff productivity
- 25% savings on bandwidth via intelligent optimization (Forbes)
Automation is not eliminating IT roles—it’s transforming them. Engineers are moving from manual device configuration to designing, orchestrating, and managing intelligent automated systems.
References
- Gartner: The State of Network Automation
- Cisco: AI-Powered Network Optimization
- Forbes: The Business Impact of Network Automation
Frequently Asked Questions
What is network automation?
It is the use of software and tools to automatically configure, manage, and maintain networks without manual intervention.
How does AI improve network automation?
AI enables predictive analytics, self-healing mechanisms, and anomaly detection that improve performance and reduce downtime.
What is the difference between SDN and traditional networking?
SDN separates control from hardware, centralizing management and improving flexibility compared to static hardware-bound setups.
What are the challenges of network automation?
Legacy systems, lack of trained staff, and misconfigured scripts can create vulnerabilities and limit automation success.
Will network automation replace engineers?
No. Engineers will shift from manual configuration to designing and managing automation strategies.