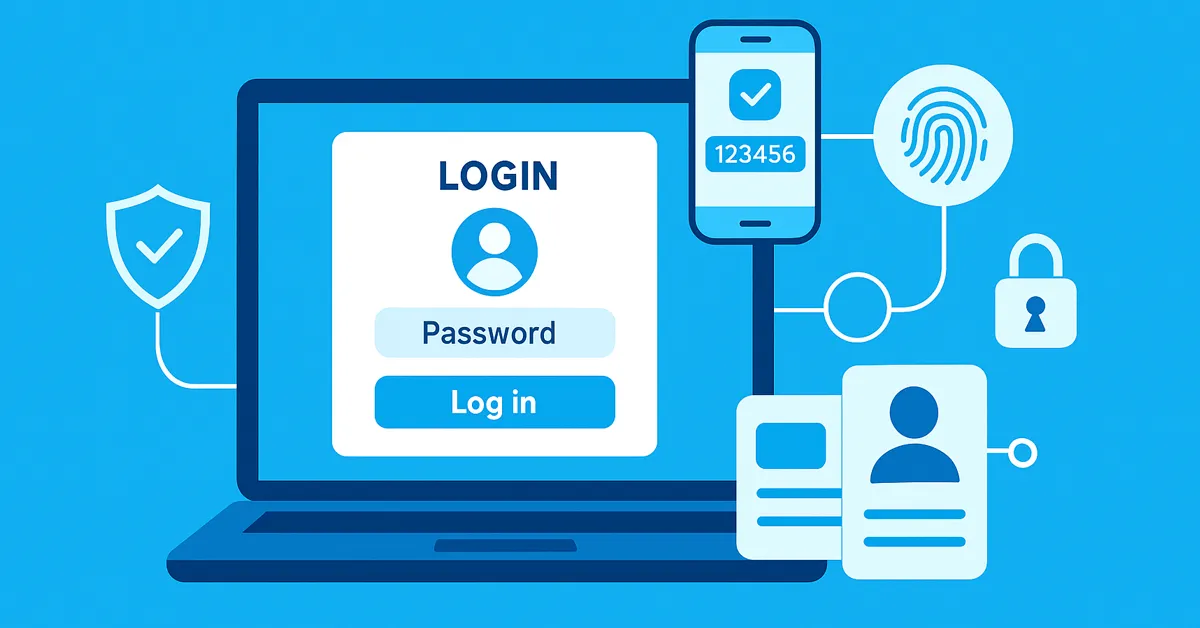
According to the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, over 80% of hacking-related breaches involve weak or stolen passwords. MFA significantly mitigates this risk by combining multiple authentication factors that verify a user’s identity.
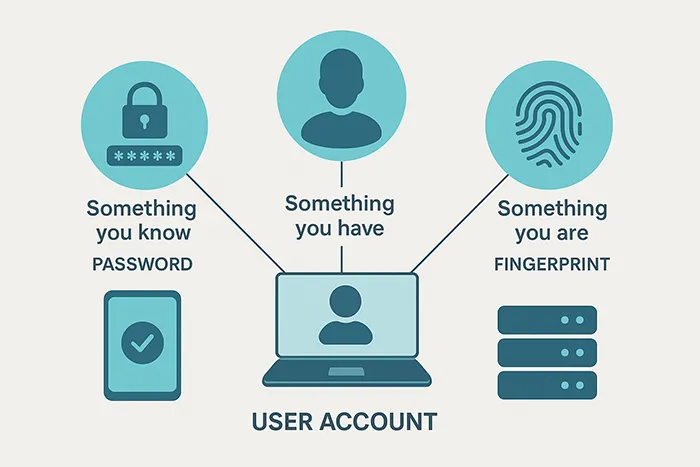
- Something you know: Password or PIN codes.
- Something you have: Smartphones, hardware tokens, or security keys.
- Something you are: Biometric data like fingerprints or facial recognition.
MFA adds resilience to access control systems — even if one factor is compromised, attackers still can’t gain entry without additional verification. This is why most Zero Trust Security architectures use MFA as a foundation.
Best Practices for Implementing MFA
1. Choose the Right Authentication Factors
Balance convenience with security. Combine at least two factors from different categories — for instance, a password (knowledge) and a hardware token (possession) or a fingerprint (inherence). This layered approach prevents most brute-force or credential-stuffing attacks.
2. Use a Trusted MFA Solution
Select an MFA platform that integrates seamlessly with your organization’s Identity and Access Management (IAM) framework. Focus on solutions offering strong encryption, adaptive authentication, and cross-platform support. Popular choices include Okta MFA, Duo Security, and Microsoft Defender for Identity.
3. Ensure Proper User Enrollment & Training
Successful MFA deployment relies on user adoption. Offer clear training and self-service registration to simplify setup. Provide backup authentication methods (such as recovery codes or secondary devices) to avoid lockouts when a user loses a phone or token.
4. Enforce MFA for High-Risk Scenarios
Use conditional access policies to mandate MFA for critical logins such as VPN connections, finance systems, and administrative accounts. Modern IAM platforms like Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) make this configuration straightforward.
5. Implement Adaptive Authentication
Adaptive authentication analyzes user context such as location, device type, and time of access to determine risk level. If a login appears suspicious, the system adds extra verification steps automatically.
Expert Recommendations for Implementing MFA
- Mandate MFA for All Accounts: Prioritize privileged and remote users first.
- Educate and Test: Train employees to recognize MFA prompts and report phishing attempts.
- Monitor Continuously: Use SIEM tools to detect anomalies in login patterns and failed authentications.
- Review Quarterly: Audit MFA policies and update settings for new apps or compliance needs.
Comparison Table: Top MFA Solutions
| Tool | Key Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duo Security | Push notifications, SMS codes, biometric support | Easy to use, excellent integration options | Costly for large organizations |
| Okta MFA | Adaptive authentication, SSO integration | Highly customizable and enterprise-ready | Steeper learning curve for new admins |
| Microsoft Defender for Identity | Integrated with Azure AD and Conditional Access | Ideal for Microsoft ecosystems | Limited support outside Microsoft environments |

Key Takeaways
- Implement MFA for all critical accounts and privileged access.
- Combine biometrics with hardware tokens for maximum security.
- Enable adaptive authentication to enhance user experience without sacrificing protection.
- Continuously review logs and update authentication methods to stay ahead of attackers.

Final Thoughts
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication is one of the most effective ways to protect your organization from credential theft. By following these best practices, you’ll not only enhance security but also maintain a smooth user experience. As cyber threats evolve, so should your authentication strategies — stay vigilant, review regularly, and keep security human-focused.
For further reading, explore our detailed guides on Zero Trust Security and Real-World Cybersecurity Lessons.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the most secure form of Multi-Factor Authentication?
Combining biometrics (fingerprint or facial scan) with hardware tokens like YubiKey provides the highest security against phishing and credential theft.
Can MFA be bypassed?
While rare, advanced phishing attacks may trick users into sharing tokens. Hardware-based keys and phishing-resistant FIDO2 standards greatly reduce that risk.
Is MFA difficult to implement?
No — most modern MFA solutions offer cloud-based setup and intuitive user enrollment. Proper training and clear documentation ensure a smooth deployment.
How often should MFA settings be reviewed?
At least quarterly. Review logs, new apps, and emerging threats to keep your authentication policies current and effective.
Does MFA affect user experience?
When implemented properly with adaptive authentication, MFA balances security and convenience without slowing workflow.