The WHEA_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR is a critical error message with stop code 0x00000124 that appears on a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) in Windows 10 and Windows 11. This error is triggered by the Windows Hardware Error Architecture (WHEA) and typically points to a severe hardware or driver issue.
Encountering a BSOD can be stressful, especially if it interrupts work or gaming. Don’t panic—this step-by-step guide will walk you through diagnosing and fixing the error using proven methods. We’ll also highlight new features in Windows 11 (2025 updates) that help detect and prevent these issues.
What Causes WHEA_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR?
This BSOD is generally linked to hardware or low-level system problems. Common causes include:
- CPU, GPU, or RAM malfunctions
- Overheating due to clogged fans or degraded thermal paste
- Driver conflicts or outdated drivers
- Unstable overclocking
- Corrupted system files
- Failing hard drives or SSDs
- Power supply issues or voltage instability
What’s New in Windows 11 (2025 Updates)
Since your article was originally published, Microsoft introduced improvements that can help prevent or troubleshoot this error:
- Windows Health Dashboard: Automatic reporting of recurring hardware errors for quicker diagnosis.
- Driver Rollback Protection: If a driver update causes instability, Windows can now revert automatically.
- Memory Integrity (Core Isolation): Provides extra protection against low-level driver crashes.
- Enhanced Reliability Counters: Logs thermal and voltage spikes in Event Viewer.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
1. Check for Overheating
Overheating remains one of the top culprits for hardware crashes. Dust buildup, old thermal paste, or failing fans can cause sudden shutdowns.

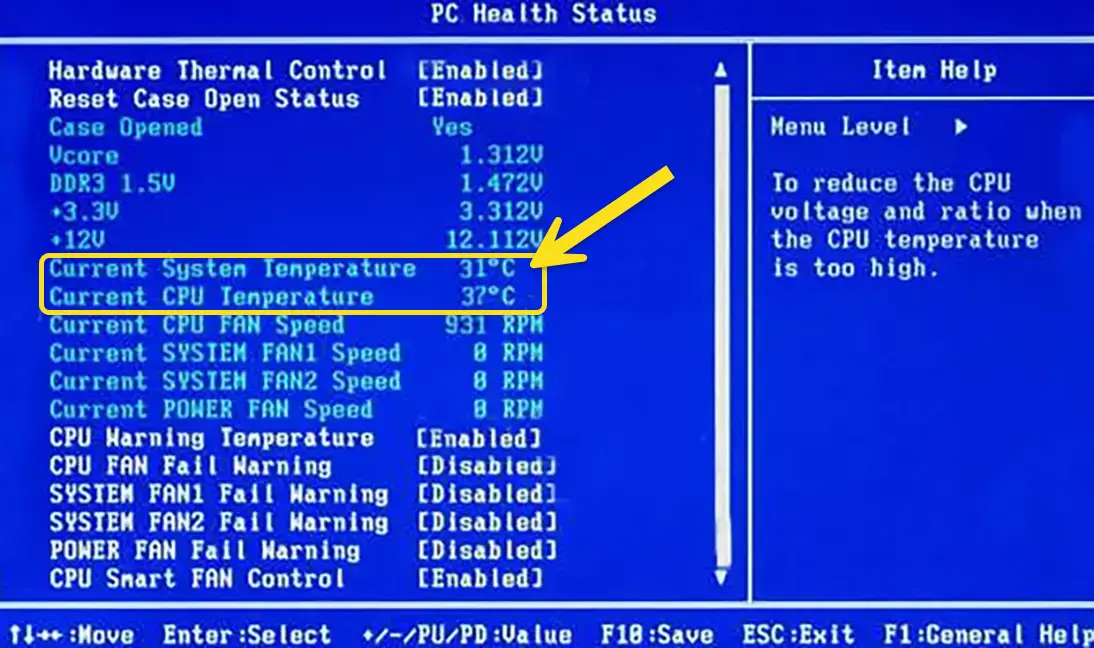
How to check CPU temperature:
- Enter BIOS/UEFI by pressing F2, F10, F12, or Del during boot.
- Check CPU temperature readings under Hardware Monitor.
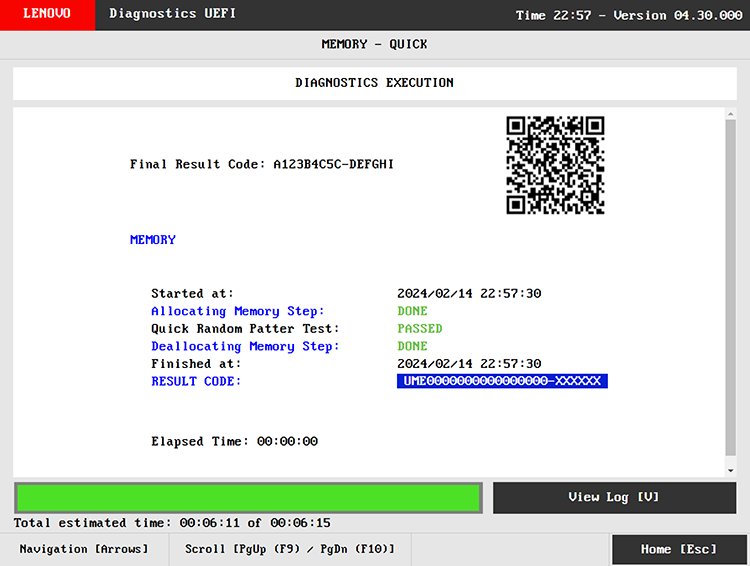
2. Run Hardware Diagnostics
Most manufacturers (Dell, HP, Lenovo) include diagnostics tools. These test RAM, storage, and CPU health.
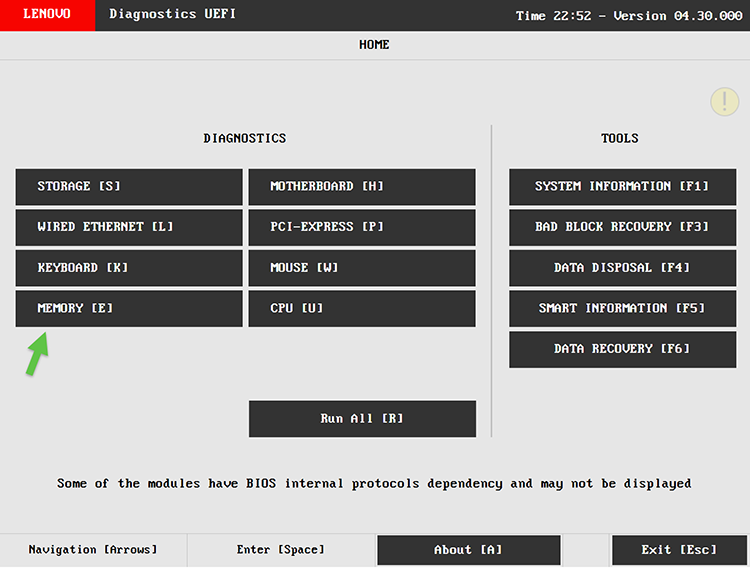
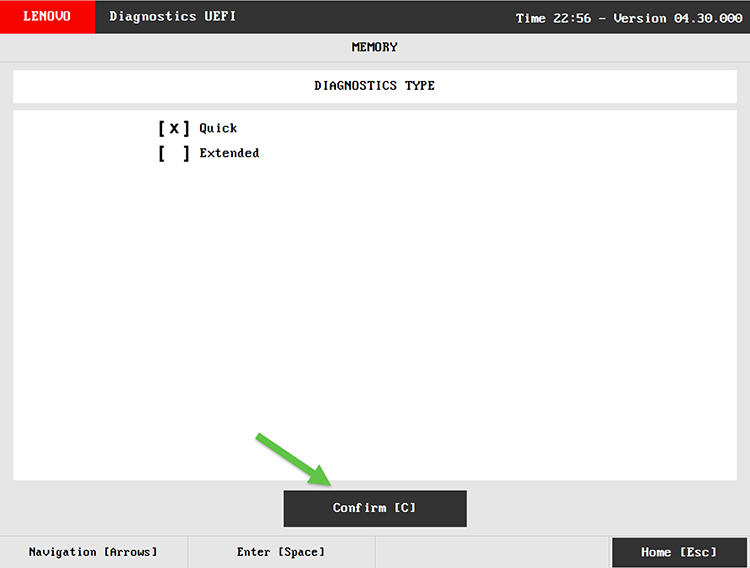
For example, on Lenovo devices:
- Press F12 during startup.
- Select Diagnostics.
- Run Memory and Storage Tests.
3. Update Drivers and Firmware
Outdated or corrupted drivers often trigger BSODs. Keeping your drivers updated ensures stability.
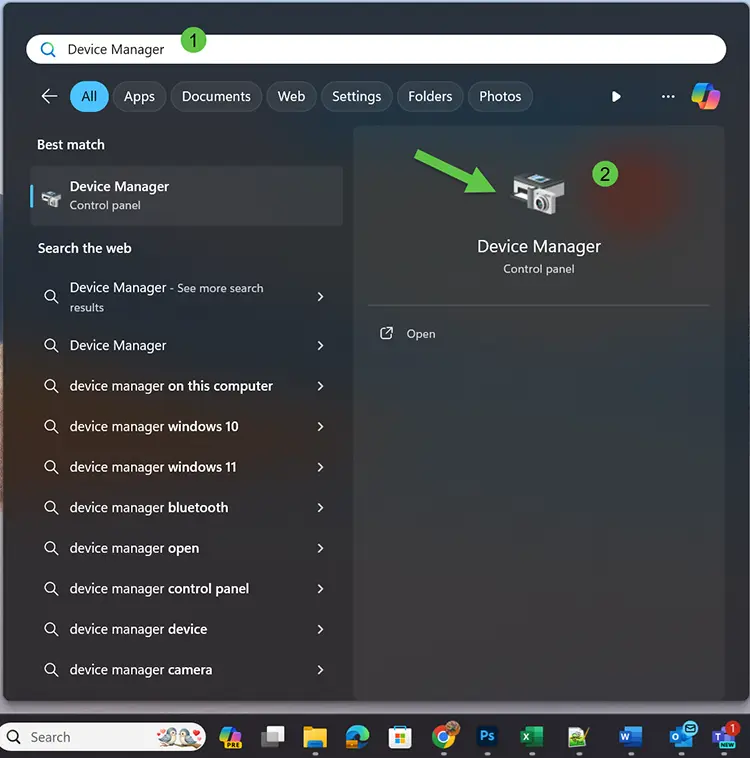
- Open Device Manager (Windows key ➔ type “Device Manager”).
- Expand hardware categories, right-click devices, select Update driver.
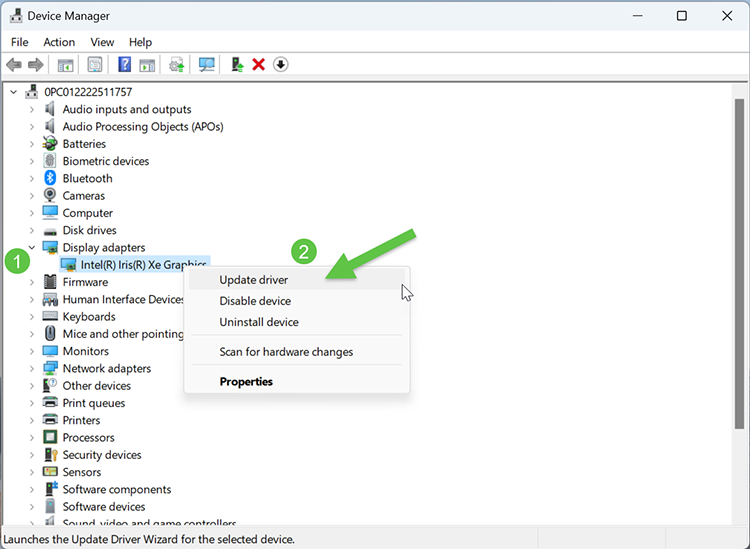
Tip: Download official drivers directly from your PC or motherboard manufacturer’s website. See Microsoft’s driver documentation for details.
4. Disable Overclocking
If your CPU or GPU is overclocked, revert to default settings in BIOS. Even moderate overclocks can trigger WHEA errors under heavy loads.
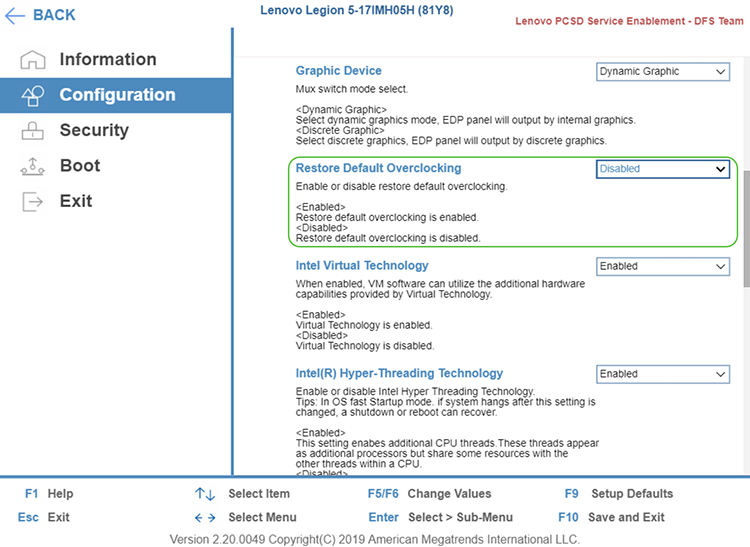
5. Repair System Files with SFC & CHKDSK
Corrupted Windows system files can also cause BSODs. Use built-in repair tools:
- Open Command Prompt (Admin).
- Run:
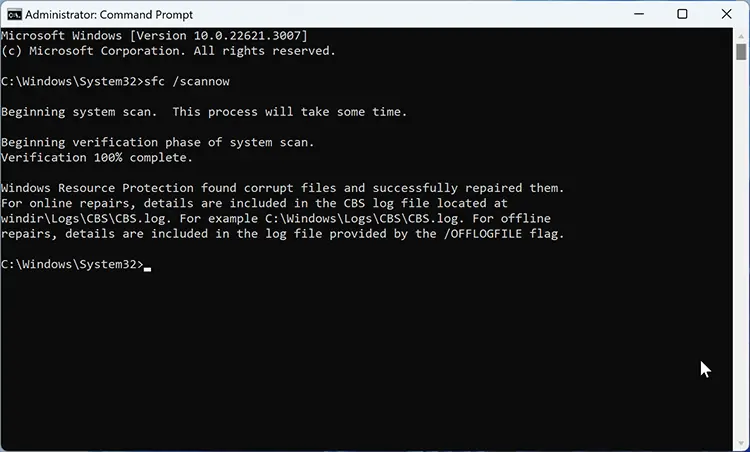
sfc /scannow - Once finished, run:
chkdsk /f /r
6. Memory & Hard Drive Tests
Faulty RAM and disks are frequent WHEA error triggers.
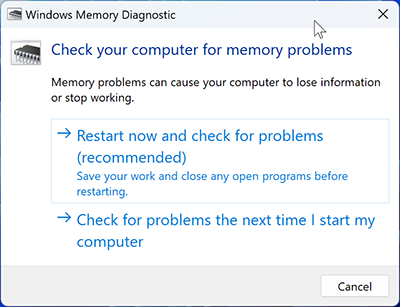
- Search Windows Memory Diagnostic in the Start menu.
- Select Restart now and check for problems.
Additional Prevention Tips
- Keep Windows updated with the latest patches.
- Replace thermal paste every 2–3 years.
- Use a reliable PSU with stable voltage.
- Choose high-quality RAM compatible with your motherboard.
- Monitor temperatures with tools like HWMonitor.
When to Seek Professional Help
If diagnostics confirm failing hardware (CPU, GPU, RAM, or motherboard) or the error persists after all fixes, it’s time to contact a certified technician or your manufacturer’s service center.
Related Articles
- How to Resolve Error 0x80004005 in Windows 10 & 11
- How to Check Overheating of Your Computer
- How to Fix a Frozen Windows and macOS Computer
- How to Clean Up Disk Space on Windows 10
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes WHEA_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR in Windows?
This error is caused by hardware malfunctions (CPU, GPU, RAM, or drives), overheating, corrupted drivers, or unstable overclocking.
Can overheating trigger this BSOD?
Yes. For example, clogged cooling fans or degraded thermal paste can raise CPU temps and trigger hardware shutdowns, resulting in this BSOD.
Is it safe to update BIOS/UEFI firmware?
Yes, if done correctly. Always follow your motherboard vendor’s instructions. Improper BIOS updates can brick your system.
Should I disable overclocking to fix this?
Yes. Returning your CPU and GPU to factory settings helps restore stability and prevents repeated BSODs.
What if diagnostics show hardware failure?
You should replace the failing component immediately. Using defective hardware risks permanent damage and data loss.